Voting Solutions for All People (VSAP)
Make / Model: Smartmatic/Los Angeles County VSAP
Equipment Type: Ballot Marking Device, Batch-Fed Optical Scanner, and Remote Ballot Marking System: Client-Side
Back to Voting Equipment Database
Overview

The VSAP voting system is composed of six core components: the Ballot Marking Device (BMD), BMD Manager (BMG), Enterprise Signing Authority (ESA), Tally high-capacity scanner (Tally), VSAP Ballot Layout (VBL), and the Interactive Sample Ballot (ISB). The VSAP system is only used in Los Angeles County, California, which owns the source code initially developed by Smartmatic.
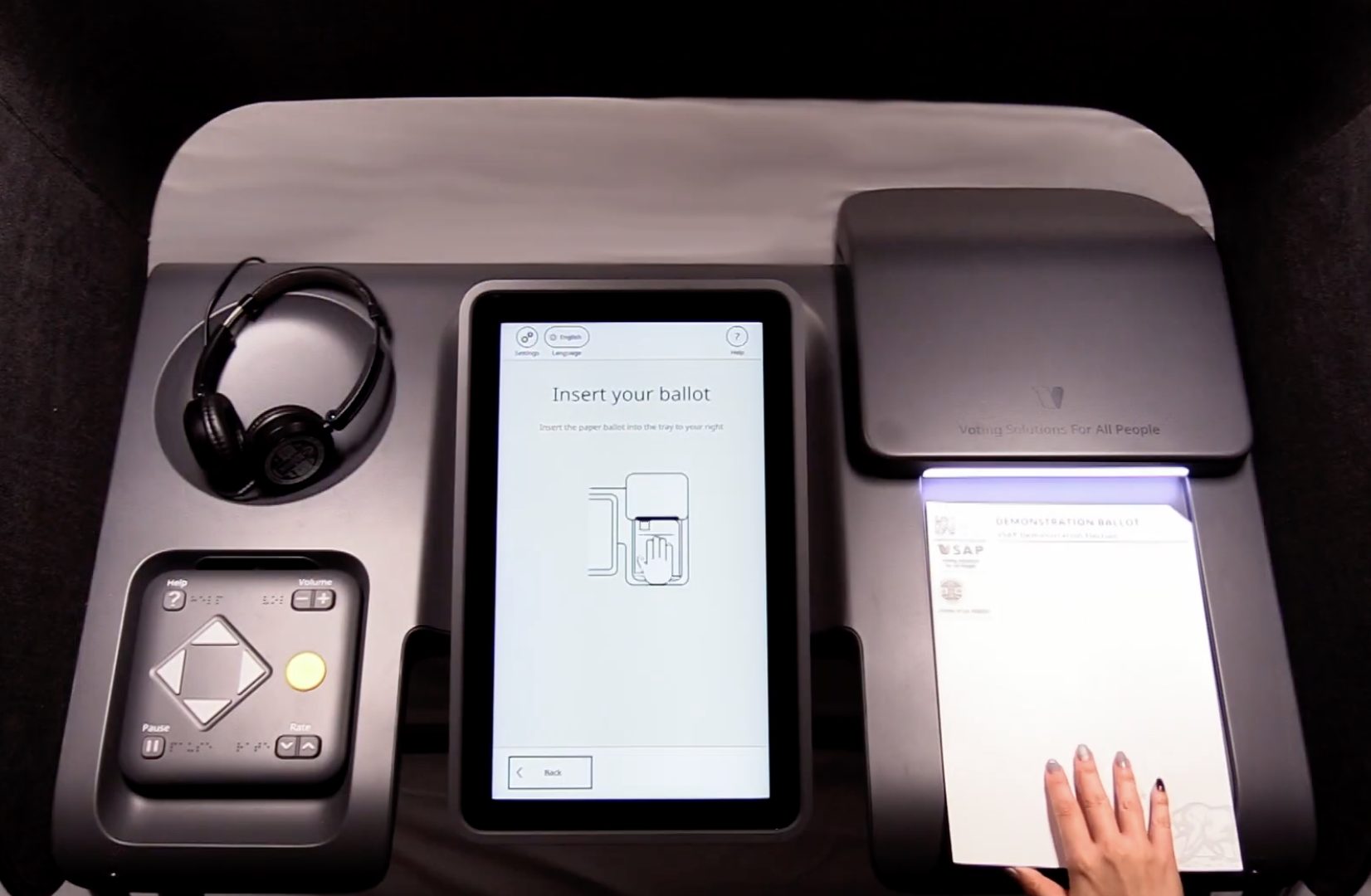
The VSAP BMD is a touchscreen ballot marking device that assists voters in marking their ballots. Every VSAP BMD features an adjustable tablet-style touchscreen, an audio-tactile interface (ATI) consisting of a controller, headphones, and dual-switch input, paper handler (scanner, printer, and tray), and QR code scanner, which voters can use to generate, verify, and cast their paper ballots. The VSAP BMD is capable of providing ballots in all languages required in the State of California. Before each election, Los Angeles County’s logic and accuracy testing includes confirming that all required languages are complete and present in the BMDs. The BMD does not tabulate; rather, the scanner components of the BMD are used to read the encoding for ballot styles, to read the Interactive Sample Ballot, or to discern that the voter has completed a ballot and is ready to verify and cast it.
The VSAP Tally scanner is a high-speed high-capacity scanner and tabulator. VSAP Tally captures and processes ballot images to digitally count votes from (mailed, BMD-marked, and ISB-created) paper ballots. VSAP Tally scans and creates images of ballots and converts ballot images into cast vote records (CVRs). Tally then tabulates the votes and enables export of the election results.
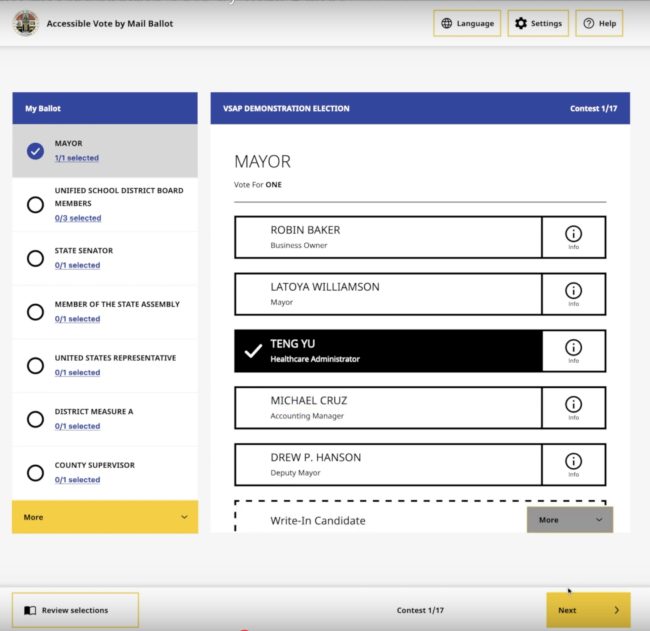
The Interactive Sample Ballot (ISB) can be used as either a remote ballot marking system or as a “poll pass,” which speeds up the voter’s time in the poll booth. The ISB does not require internet connection for making selections. Initially, the ISB client-side remote ballot marking system was available only to Uniformed and Overseas Citizens Absentee Voting Act (UOCAVA) voters and voters with disabilities; however, it was made available to all voters before the November 2020 election. This system can only be used to mark and print a ballot for drop off or mail return—the electronic submission of voted ballots (internet voting) is not supported.
Voting Process
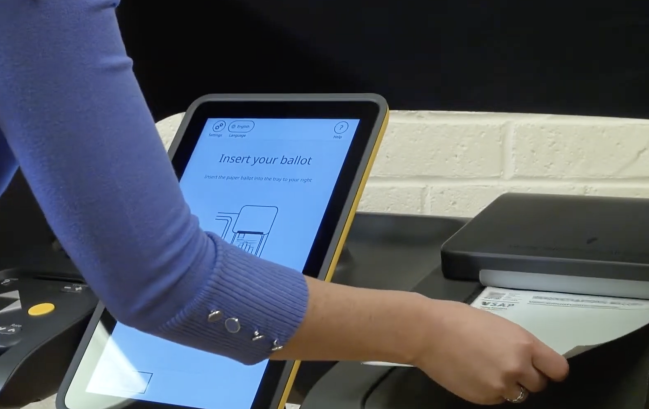


Voters can use the Interactive Sample Ballot (ISB) as a “poll pass” by marking their selections on a sample ballot on their computer or mobile device. The ISB encodes their selections in a QR code, which the voter later scans on a BMD at the polling place. The BMD then populates the voter’s ballot with their pre-selected choices. The voter can then make any desired changes to their selections via the BMD, or can accept their selections and proceed to printing, verification, and casting.
When a voter successfully checks in at their voting location, they are provided with a blank ballot on which is printed a header encoded with the election and ballot style information corresponding to the voter’s address. (Los Angeles County elections have hundreds of thousands of ballot styles.) The voter then inserts their ballot into the VSAP Ballot Marking Device (BMD) to activate the voting session. The BMD prints marked ballots in a full-size page summary list format (selections only) showing each contest and the voter’s choices, and also encodes voter selections into a digitally-signed, non-proprietary, non-human readable QR code. The California Secretary of State requires poll worker training on voter verification of QR codes. The ballot is presented and held in a tray. After the voter has an opportunity to verify their ballot, the ballot is fed back from the tray into the integrated ballot box, where it is stored until election workers detach the integrated ballot box to transport ballots for counting. Election workers empty the boxes throughout the day as needed.
Interactive Sample Ballot (ISB) as a Remote Ballot Marking System
The ISB can also be used as a remote ballot marking system for voters with disabilities. Eligible voters access the system in their preferred browser on their computer or mobile device. Voters enter their last name, date of birth, and house number. The voter marks their ballot using the client-side remote ballot marking system, confirms their selections on the review screen, and prints their ballot to return via mail or drop off. The ISB does not support the electronic return of voted ballots (internet voting).
Videos
Voting Solutions for All People (VSAP) Voting Instruction Video
How to Use and Return an Accessible Vote by Mail Ballot
Guide to the Voting Soutions for All People (VSAP) Ballot Marking Device
Resources
References
VSAP Testing and Certification Documents, California Secretary of State
Los Angeles County VSAP 3.0 California Use Procedures, County of Los Angeles (2022)
Los Angeles County VSAP 3.0 Approval, California Secretary of State (2022)
Los Angeles County VSAP 3.0 Consultant’s Functional Test Report, SLI Compliance (2022)
Los Angeles County VSAP 3.0 Consultant’s Software Test Report, SLI Compliance (2022)
Los Angeles County Voting Solutions for All People (VSAP) 3.0 Security and Telecommunications Test Report for California Secretary of State, SLI Compliance (2022)
Los Angeles’ County Voting Solutions for All People (VSAP) 3.0 Voting System Accessibility, Usability, and Privacy Test Report for California Secretary of State, SLI Compliance (2022)
Baseless Conspiracy Theory Targets Another Election Technology Company, Saranac Hale Spencer, FactCheck.org (Nov. 25, 2020)
Los Angeles County’s risky voting experiment, POLITICO (March 3, 2020)
California Secretary of State Consultant’s Public Report on Security and Telecommunications Testing of the LA County VSAP 2.0 Voting System, Freeman, Craft, McGregor Group (2019)
The company behind LA’s new election infrastructure Saul Gonzalez, KCRW (2018)
Security Concerns
After a voter reviews their BMD-marked ballot, the ballot is sent back to the attached ballot box via the same path from which the ballot is printed—i.e., the ballot passes under the machine’s printer head. The printer head is raised when the ballot comes back through the machine; however, if the system is hacked to lower the printer head, the printer could alter the voter’s choices without the voter knowing.
Manufacturer Profile
![]()
Smartmatic USA
1001 Broken Sound Pkwy, Suite D
Boca Raton FL 33487
(561) 862-0747
usa@smartmatic.com
https://www.smartmatic.com/
Smartmatic is a global election technology provider, founded by Antonio Mugica, Roger Piñate and Alfredo Anzola in 2000 in the United States. In 2005, Smartmatic purchased Sequoia Voting Systems; in 2007, it sold the subsidiary. Over the years, Smartmatic has designed and implemented voting technologies in nearly 35 countries. The company is headquartered in London, United Kingdom, with its U.S. headquarters in Boca Raton, Florida. Smartmatic was selected to build Los Angeles County’s Voting Solutions for All People (VSAP) program in 2018, with the system officially launched in 2020. Los Angeles County owns the source code. Smartmatic continues to provide products and services for local, municipal, and state elections each year.